Chapter 8 Multiple Choice Type Questions
Question 1.
If the distance between two magnetic poles of unit magnetic strength is 1 m, then force acting between them will be:
(a) 4π × 10-7 N
(b) 4π N
(c) 10-7 N
(d)

N
Answer:
(c) 10-7 N
Question 2.
Magnetic susceptibility for superconductors is :
(a) +1
(b) -1
(c) zero
(d) infinity
Answer:
(b) -1
For superconductors, value of magnetic susceptibility is -1.
Question 3.
Magnetic susceptibility of free space is :
(a) +1
(b) -1
(c) zero
(d) infinity
Answer:
(c) zero
Magnetic susceptibility of free space is zero.
Question 4.
Magnetic susceptibility is negative and very less for :
(a) ferromagnetic substances
(b) paramagnetic substances
(c) diamagnetic substances
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(c) diamagnetic substances
For diamagnetic substances.
Question 5.
If the relative permeability of a substance is 1.00001, then substance will be :
(a) ferromagnetic
(b) paramagnetic
(c) diamagnetic
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) paramagnetic
As μr > 1, so substance should be paramagnetic.
Question 6.
Unit of magnetic moment is :
(a) Wb
(b) Wb/m2
(c) A/m
(d) Am2
Answer:
(d) Am2
Unit of magnetic moment is Am2
Question 7.
Wb × A/m is equals to :
(a) J
(b) N
(c) H
(d) W
Answer:
(b) N
Wb ×

is equal to N.
Question 8.
In which of the following, the magnetic field does not interplay with :
(a) magnet
(b) accelerated magnet
(c) static charge
(d) dynamic charge
Answer:
(c) static charge
Magnetic field does not interact with static charges.
Question 9.
The cause of dimegnetism is :
(a) orbital motion of electrons
(b) spin motion of electrons
(c) paired electrons
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) orbital motion of electrons
Due to orbital motion of electrons.
Question 10.
Magnetic moment of diamagnetic substances is :
(a) infinity
(b) zero
(c) 100 Am2
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) zero
Magnetic moment of diamagnetic substance is zero.
Question 11.
The relative permeability of ferromagnetic substance is :
(a) μr > 1
(b) μr >> l
(c) μr = 1
(d) μr = 0
Answer:
(b) μr >> l
For ferromagnetic substance μr >> l .
Question 12.
Vertical component of earth’s magnetic field is zero at:
(a) magnetic pole
(b) geographical pole
(c) magnetic meridian
(d) none of these
Answer:
(d) none of these
None of the option is correct.
Question 13.
Area of hysteresis loop of any substance represent:
(a) energy loss in magnetising a substance in unit cycle
(b) energy loss in magnetising unit volume in unit cycle
(c) energy loss in magnetising a substance for unit volume
(d) energy loss in magnetising a substance
Answer:
(d) energy loss in magnetising a substance
Energy loss in magnetising a substance.
Question 14.
Steel is used for making permanent magnet because :
(a) energy loss is minimum
(b) density of steel is more
(c) residual magnetism of steel is more
(d) due to external magnetic field the magnetism does not destroy easily
Answer:
(d) due to external magnetic field the magnetism does not destroy easily
Its magnetism does not destroy easily by external magnetic field.
Question 15.
At Curie temperature, ferromagnetic substance becomes: .
(a) paramagnetic
(b) diamagnetic
(c) ferromagnetic
(d) more ferromagnetic
Answer:
(c) ferromagnetic
Paramagnetic.
Chapter 8 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
A magnetic needle which is free to rotate in a vertical plane if placed at geomagnetic south or north pole, then in which direction it rotates?
Answer:
Free magnetic needle in vertical plane always indicate in vertical up or down.
Question 2.
Name the magnetic substance whose nature does not change by changing the normal temperature.
Answer:
The magnetic behaviour of diamagnetic substance does not change by changing the normal temperature.
Question 3.
On going from equatorial line towards pole what will be the change in angle of dip?
Answer:
On going from magnetic equatorial line towards poles, the angle of dip increases from 0° to 90°. On magnetic equatorial line dip angle is 0° and at poles it will be 90°.
Question 4.
The magnetic susceptibility of substance is – 0.085. What type of substance this is?
Answer:
Diamagnetic substance. Because for diamagnetic substance, magnetic susceptibility is negative and always less than.
Question 5.
Define retentivity.
Answer:
The magnetic induction left behind in the sample after the magnetising field has been removed is called residual magnetism or rententity.
Question 6.
Give two examples of paramagnetic substances.
Answer:
(i) CuCl2 (ii) Oxygen.
Question 7.
What is magnetic meridian?
Answer:
The vertical plane passing through the magnetic axis of a freely suspended small magnet is called magnetic meridian. The earth’s magnetic field acts in the direction of the magnetic meridian.
Question 8.
The angles of dip at two places on the surface of the earth are respectively 0° and 90°, where are these places located?
Answer:
On magnetic equatorial line angle of dip is 0° and at pole, angle of dip is 90°.
Question 9.
Write a relation between magnetic permeability of a medium and magnetic susceptibility.
Answer:
μr = (1 + Xm)
μr — magnetic permeability
Xm — magnetic susceptibility
Question 10.
Write unit of magnetic pole strength.
Answer:
The unit of magnetic pole strength is (A-m).
Question 11.
The vertical component of earth’s magnetic field at a place is V3 times the horizontal component. What is the value of angle of dip at this place?
Answer:
Question 12.
What is magnetic hysteresis?
Answer:
The phenomenon of the lagging of magnetic induction behind the magnetising field when a specimen of magnetic material is subjected to a cycle of magnetization is called hysteresis.
Question 13.
What will be the ratio in the values of magnetic field due to a bar magnet at axial and equatorial positions from mid point of bar magnet?
Answer:
Magnetic field in axial line
Question 14.
What will be the value of angle of 4ip where horizontal and vertical component of earth are equal?
Answer:
BH = BV (given)
tanθ =

= 1
tanθ = tan45°
Question 15.
If a bar magnet is cut along its length in two equal parts, then what will be the change in magnetic moment of the magnet?
Answer:
Magnetic Moment of a Bar Magnet
Magnetic moment of a bar magnetic is defined as the product of pole strength of pole and the separation between poles. If the pole strength is consider to be m and dipole length is l then :
M = m × l
The direction of M is from S pole to N pole.
It a bar magnet cut transversely
Chapter 8 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
A bar magnet is placed in a uniform magnetic field such that its magnetic moment makes angle α with the direction of

. Derive a expression for its potential energy.
Answer:
Potential Energy of a Magnetic Dipole
As τ = MB sinθ
If the dipole is rotated against the action of this torque, work has to be done. This work is stored as potential energy of the dipole.
The work done in turning the dipole through a small angle dθ is
dW = τdθ = MB sinθdθ
If the dipole is rotated from an initial position θ = θ1 to the final position θ = θ2, then the total work done will be
W =
![\int d W=\int_{\theta_{1}}^{\theta_{2}} M B \sin \theta d \theta=-M B[-\cos \theta]_{\theta_{1}}^{\theta_{2}} \int d W=\int_{\theta_{1}}^{\theta_{2}} M B \sin \theta d \theta=-M B[-\cos \theta]_{\theta_{1}}^{\theta_{2}}](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Cint+d+W%3D%5Cint_%7B%5Ctheta_%7B1%7D%7D%5E%7B%5Ctheta_%7B2%7D%7D+M+B+%5Csin+%5Ctheta+d+%5Ctheta%3D-M+B%5B-%5Ccos+%5Ctheta%5D_%7B%5Ctheta_%7B1%7D%7D%5E%7B%5Ctheta_%7B2%7D%7D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0)
= -MB(cosθ2 – cosθ1)
This work done is stored as the potential energy U of the dipole.
∴ U = -MB(cosθ2 – cosθ1)
The potential energy of the dipole is zero when

. So the potential energy of the dipole in any orientation θ can be obtained by putting θ
1 = 90° and θ
2 = θ in the above equation.
∴ U = -MB(cosθ – cos 90°)
or U = -MBcosθ = – M. B
Question 2.
How can you distinguish between diamagnetic and paramagnetic rods?
Answer:
When suspended freely in a magnetic field,
- the paramagnetic rod sets itself parallel to the field, and
- the diamagnetic rod itself perpendicular to the field.
Question 3.
Why do we get two neutral points for a bar magnet? Can we obtain only one neutral point? Why?
Answer:
Neutral point is the point where the magnetic field due to magnet is equal and opposite to the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field. The resultant magnetic field at the neutral point is zero. In this way two neutral points are obtained.
On placing the north pole or south pole of bar magnet downwards in vertical position, we found out only one neutral point whose position is from north pole to south or south towards north.
Question 4.
Why soft iron is used in making electromagnet?
Answer:
Soft iron is preferred in electromagnets because of its
- high permeability and
- low retentivity and coercivity.
Question 5.
A bar magnet is placed in parallel to a magnetic field
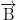
. Its magnetic moment is

. How much work will be done by magnetic moment to make it perpendicular to magnetic field?
Answer:
Given, θ1 = 0°
later θ2 = 90°
W = MB(cosθ1 – cosθ2)
= MB( cos 0°- cos 90°)
= MB( 1 – 0)
⇒ W = MB (maximum unstable condition)
Question 6.
Define angle of declination and angle of dip?
Answer:
Angle of declination : The angle between the geographical meridian and the magnetic meridian at a place is called the magnetic declination at that place.
Angle of dip : The angle made by the earth’s total magnetic field
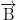
with the horizontal direction in
the magnetic meridian is called angle of dip (δ) at any place.
Question 7.
Write Curie-Weiss law and what is Curie temperature for iron?
Answer:
Curie-Weiss law : Above the Curie point i.e., in the paramagnetic phase, the susceptibility varies with temperature as
X
m =

(T > T
C)
Where C’ is a constant. This is modified Curie’s law for a ferromagnetic material above the Curie temperature. It is also known as Curie-Weiss law.
Curie temperature for iron is 1043 K.
Question 8.
Write four characteristics of magnetic field lines?
Answer:
Magnetic Field Lines or Magnetic Lines of Force
The path made by a compass needle in going it from one end of the bar magnet to another end, then magnetic lines of force may be defined as the curve, the tangent at any point gives the direction of the magnetic field at that point. It may also be defined as the path along which a unit north pole would tend to move if free to do so. Magnetic lines of force are shown in figure 8.7.
Properties
- The magnetic field lines of a magnet forms continuous closed loops.
- They start in air from the N-pole and end at the S-pole and then return to the N-pole through the interior of the magnet.
- The tangent to the field line at a given point represents the direction of the net magnetic field B at that point.
- The magnetic field lines do not intersect each other. If they do so, that would mean there are two directions of the magnetic field at the point of intersection, which is impossible.
- The larger the number of field lines crossing per unit area, the stronger is the magnitude of the magnetic field. Near from poles, the magnetic field is stronger and far from poles, the magnetic field is weak.
- In uniform magnetic field, magnetic field lines are at parallel and at same distance.
Question 9.
What are the behaviour of diamagnetic, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic substances in non-uniform magnetic field?
Answer:
- When placed in a non-uniform magnetic field, a diamagnetic substance moves from stronger to the weaker parts of the field.
- When placed in a non-uniform magnetic field, a paramagnetic substance moves from weaker to the stronger parts of the field.
- When a ferromagnetic substance is placed in non-uniform magnetic field, it moves from weaker to the stronger parts of the field.
Question 10.
What is Gauss’s law in magnetism? What does it represent?
Answer:
Gauss’s law in magnetism : It states that the surface integral of the magnetic field (

) over a closed surface S is equal zero.
Gauss’s law indicates that there are no sources or sinks of magnetic field inside a closed surface.
Question 11.
Magnetic lines of force form closed curve. Why?
Answer:
The direction of magnetic field lines outside magnet is from N to S pole while inside is S to N pole. So they form closed magnetic field lines.
Question 12.
Compare the magnetic fields of a bar magnet and current carrying solenoid.
Answer:
Comparison of bar magnet and solenoid :
Similarities :
- Both when hang freely stops in N-S direction.
- Both attract magnetic substances.
- Both have two poles-N pole and S pole.
- Like poles repel and unlike poles attract in both of them.
- Both show phenomenon of induction.
Dissimilarities
| Bar Magnet | Solenoid |
| 1. | Magnetism is strong at its ends and minimum at middle. | They have uniform magnetism inside while at ends it is feeble. |
| 2. | Polarity remain constant. | Polarity at ends depends on direction of flow of current. |
| 3. | They have stable magnetism. | Its magnetism depends on the value of flowing current. |
Question 13.
Explain the possible cause of earth’s magnetism.
Answer:
Our planet’s magnetic field is believed to be generated deep down in the earth’s core. The coroiolis force, resulting from the earth’s spin also causes swirling whirl pools. This flow of liquid iron generates electric current, which in turn produce magnetic fields.
Question 14.
What are the uses of hysteresis curve?
Answer:
A study of B-H loops reveals the following informations :
(i) For a given H, B is more for soft iron than steel. So soft iron has a greater permeability.
(ii) As permeability of soft iron is greater than steel, so soft iron has a greater susceptibility than steel.
(iii) The retentivity of soft iron is greater than the retentivity of steel.
(iv) The coercivity of soft iron is less than the coercivity of steel.
Question 15.
Deduce the expression for magnetic dipole moment of a bar magnet placed in a uniform magnetic field at angle θ. When is it maximum?
Answer:
Torque on a Bar Magnet in Uniform Magnetic Field ;
Consider a bar magnet NS of dipole length 2l placed in a uniform magnetic field
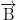
. Let m be the pole strength of its each pole. Let the magnetic axis of the bar magnet make an angle θ with the magnetic field
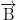
, as shown in figure 8.17 (b).
Force on N-pole = mB, along
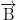
Force on S-pole = mB, opposite to
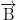
The force on the two poles are equal and opposite. They form a couple, moment of couple or torque is given by relation
τ = force × perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation
= mB × 2lsinθ
= (m × 2l)Bsinθ
or τ = MBsinθ ……………. (1)
where, M = m × 2l is the magnetic dipole moment of the bar magnet.
In vector notaion,

……………. (2)
Special Cases :
(i) When bar magnet is parallel to magnetic field (θ = 0), then
τ = MBsin0 = 0
(ii) When bar magnet is perpendicular to magnetic field (θ = 90°), then
τmax = MB sin 90°= MB
The dirction of the torque

is given by the right hand screw rule as indicated in the figure 8.18. The effect of the torque

is to make the magnet align itself parallel to the field
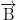
. That is why a freely suspended magnet aligns itself in the N-S direction because the earth has its own magnetic field which exerts a torque on the magnet tending it to align along the field.
Definition of Magnetic Dipole Moment: If in equation (1), B = 1, θ = 90° , then τ = M
Hence the magnetic dipole moment may be defined as the torque acting on a megnetic dipole placed perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of unit strength,
SI Unit of Magnetic Moment
Chapter 8 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name and define three elements required to specify the earth’s magnetic field at a given place. Draw a labelled diagram to define these elements.
Answer:
Elements of Earth’s Magnetism
The earth’s magnetic field at a place can be completely described by three parameters which are called elements of earth’s magnetic field. They are :
(i) Angle of declination
(ii) Angle of dip
(iii) Horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field.
(i) Angle of Declination : The angle between the geographical meridian and the magnetic meridian at a place is called angle of declination at that place. Geographic meridian is the vertical plane passing through the geographical north and south poles. While magnetic meridian is the vertical plane passing through the magnetic axis of a freely suspended small magnet.
Magnetic declination arises because the magnetic axis of the earth does not coincide with its geographic axis.
By knowing declination, we can determine the vertical plane in which the earth’s magnetic field lies. In India, the value of angle of declination is small. It is 0°41′ E for Delhi and 0°58′ W for Mumbai.
(ii) Angle of dip : The angle made by the earth’s total magnetic field  with the horizontal direction in the magnetic meridian is called angle of dip at any place. The angle of dip is different at different places on the surface of the earth. The angle between the horizontal and the final direction of the dip needle gives the angle of dip at that given location.
with the horizontal direction in the magnetic meridian is called angle of dip at any place. The angle of dip is different at different places on the surface of the earth. The angle between the horizontal and the final direction of the dip needle gives the angle of dip at that given location.
At the magnetic equator, the dip needle rests horizontally so that the angle of dip is zero at the magnetic equator. The dip needle rests vertically at the magnetic poles so that the angle of dip is 90° at the magnetic poles. At all other places, the dip angle lies between 0° and 90°.
(iii) Horizontal component of earth’s
magnetic Held : It is the component of the earth’s total magnetic field

in the horizontal direction in the magnetic meridian. If θ is the angle of dip at any place, then the horizontal component of earth’s field

at that place is given by
and tanθ =

or BV = BH tanθ …………. (3)
Question 2.
What do you mean by magnetic hysteresis curve? Draw hysteresis curve and define terms related to it.
Answer:
Magnetic Hysteresis Curve
The relation between B and H in ferromagnetic materials is complex. It is often not linear and it depends on the magnetic history of the sample. Figure 8.31 depicts the behaviour of the material as we take it through one cycle of magnetisation. Let the material be unmagnetised initially. We place it in a solenoid and increase the current through the solenoid. (Figure 8.30). The magnetic field B in the material rises and saturates as depicted in the curve Oab. This behaviour represents the alignment and merger of domains until no further enhancement is possible. It is pointless to increase the current (and hence the magnetic intensity H) beyond this. Next, we decrease H and reduce it to zero. At H = 0, B ≠ 0. This is represented by the curve Oc. The value of B at H = 0 is called retentivity or remanence. In figure 8.31, BR ~ 1.2 T, where the subscript R denotes retentivity. The domains are not completely randomised even though the external driving field has been removed. Next, the current in the solenoid is reversed and slowly increased. Certain domains are flipped until the net field inside stands nullified. This is represented by the curve cd. The value of H at d is called coercivity. As the reversed current is increased in magnitude, we once again obtain saturation. The curve Od depicts this. Next, the current is reduced (curve ef) and reversed (curve eb). The cycle repeats itself. Note that the curve Ob does not retrace itself as H is reduced. For a given value of H, B is not unique but depends on previous history of the sample. This phenomenon is called hysteresis.
Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into two categories.
1. Soft ferromagnetic materials
2. Hard ferromagnetic materials
Soft ferromagnetic materials have narrow hysteresis loop. Consequently, they have low retentivity, low coercivity and low hysteresis loss. But they have high relative magnetic permeability. Hard ferromagnetic materials have wide hysteresis loop. Consequently, they have high retentivity, high coercivity and large hysteresis loss.
A study of B-H loops reveals the following informations :
(i) For a given H, B is more for soft iron than steel. So soft iron has a greater permeability.
(ii) As permeability of soft iron is greater than steel, so soft iron has a greater susceptibility than steel.
(iii) The retentivity of soft iron is greater than the retentivity of steel.
(iv) The coercivity of soft iron is less than the coercivity of steel.
Question 3.
Explain paramagnetism and specify its characteristics. Write five differences between diamagnetic and paramagnetic substance.
Answer:
Paramagnetic Substances
Paramagnetic substances are those which develop feable magnetisation in the direction of the magnetising field. Such substances are feebly attracted by magnets and tend to move from weaker to stronger parts of a magnetic field.
Examples : Aluminium (Al), chromium (Cr), manganese, (Mn), platinum (Pt), Ca, Sb, Na, Li, Mg Tungsten, copper chloride, salt solution etc.
Explanation of Paramagnetism
According to Langevin, the atoms or molecules of a paramagnetic material possess a permanent magnetic moment either due to the presence of some unpaired electron or due to the non-cancellation of the spins of two electrons because of special reason. In the absence of an external magnetic field, the atomic dipoles are randomly oriented due to their ceaseless random motion, as shown in figure 8.27 (a). There is no net magnetisation.
When a strong enough field is applied and the temperature is low enough, the field tends to align the atomic dipoles in its own direction, producing a weak magnetic moment in the direction of magnetic field. The material tends to move from a weak field region to a strong field region. This phenomenon is paramagnetism.
When a paramagnetic material is placed in a magnetic field, the lines of force prefer to pass through it than through the surrounding air i. e., the lines of force get slightly more concentrated inside the material, as shown in figure. When a glass pot containing a paramagnetic liquid is placed over two closely lying opposite poles of magnet, the liquid accumulates and elevates in the middle and thins out near the poles. When the poles are moved apart the field at the poles becomes stronger than that at the centre and the liquid moves towards the poles.
Experimentally, the intensity of magnetisation of a paramagnetic substance is proportional to magnetic field B0 and inversely proportional to temperature T.
Diamagnetic Substances
Diamagnetic substances are those which develop feable magnetisation in the opposite direction of the magnetising field. Such substances are feebly repelled by magnets and tend to move from stronger to weaker parts of a magnetic field.
Examples : Cu, Zn, Sb, Bi, Hg, H2, N2, Au, Ag, Pb, air water, diamond silicon, quartz, alcohol, marble, glass, helium, argon, salts like sodium choride etc.
Explanation of Diamagnetism
The simplest explanation for diamagnetism is as follows. Electrons in an atom orbiting around nucleus possess orbital angular momentum. These orbiting electrons are equivalent to current-carrying loop and thus possess orbital magnetic moment. Diamagnetic substances are those in which resultant magnetic moment in an atom is zero. When magnetic field is applied, those electrons having orbital magnetic moment in the same direction slow down and those in the opposite direction speed up. This happens due to induced current in accordance with Lenz’s law, which you will study later. Thus, the substance develops a net magnetic moment in opposite direction to that of the applied field and hence repulsion.
The most exotic diamagnetic materials are super conductors. These are metals, cooled to a very low temperature which exhibits both perfect conductivity and perfect diamagnetism. Here the field lines are completely expelled. The susceptibility Xm of diamagnetic materials is small and negative. The relative permeability μr(1 + Xm) is positive but less than 1 for a diamagnetic material. A superconductor repels a magnet and is repelled by the magnet. The phenomenon of perfect diamagnetism in superconductors is called the Meissner effect.

When a glass pot containing a diamagnetic liquid is placed between two closely lying (3 – 4 mm apart) poles of a magnet, the liquid is found to move towards the poles causing a depression in the middle. This indicates that the field is stronger in the middle than that near the poles. Now if the poles are moved apart sufficiently, the magnetic field at the middle becomes weaker than that near the poles. Consequently the liquid accumulates in the middle and becomes thin near the poles.
Question 4.
What is Curie temperature? How magnetic susceptibility of dia, para and ferro magnetic substances depend on temperature? Explain and write essential law for it.
Answer:
Curie Law and Curie Temperature
The magnetic susceptibility of a paramagnetic material varies inversely as the absolute temperature,
where, C is a constant called the Curie constant and this equation is known as Curie’s law.
The susceptibility of ferromagnetic material decreases with temperature in accordance with Curie-Weiss law.
X
m =

……………… (1)
here, TC is Curie temperature of Ferromagnetic substances.
Curie Temperature : The temperature of transition from ferromagnetism to paramagnetism is called the Curie temperature TC. Table 1 lists the Curie temperatures of certain ferromagnets. The susceptibility above the Curie temperature i.e., in the paramagnetic phase is described by
X =

(T > T
C)
Table 1: Curie Temperature Tc of some Ferromagnetic Materials
| Material | Tr (K) |
| Cobalt | 1394 |
| Iron | 1043 |
| Nickel | 631 |
| Gadolinium | 317 |
Question 5.
How will you select materials for making electromagnets and permanent magnets? Write their uses also.
Answer:
The material used for making cores of electromagnets should have high initial permeability, low retentivity. Electromagnets are used in telephone, electric bell, electric motor, dynamo, communication and they are also used to separate magnetic substances from mixtures.
The material used for making permanent magnets must have high retentivity, high coercivity and high permeability. They are used in galvanometer, ammeter, voltmeter and loudspeaker.
Suitable materials for making permanent magnets are
Cobalt steel : Fe + Co + W+ Cr + Mn + C
Carbon steel : Fe + C + Mn
Alnico : Fe + Al + Ni + + Co + Cu
Ticonal : Co + Fe + Ni + Al + Ti + Cu
The material used for making cores of transformers must have high initial permeability, low hysteresis loss and low retentivity. Permalloy is best alloy for this. Also transformer steel (4% silicon in soft iron), Mumetal (Fe + Cu + Ni + Mn) are also used in making transformer core.
Electromagnet: As shown in figure 8.33, take a soft iron rod and wind a large number of turns of insulated copper wire over it. When we pass a current through the solenoid, a magnetic field is set up in the space within the solenoid. The high permeability of soft iron increases the field one thousand times. The end of the solenoid at which the current in the solenoid seems to flow anticlockwise acts as N pole and other one as S-pole. When the current in the solenoid is switched off, the soft iron rod looses its magnetism almost completely due to its low retentivity.
Properties of Electromagnets
1. The materials which have low retentivity.
2. The materials which have high permeability
Permanent magnets : Permanent magnets are made of the materials which have high retentivity high coercivity and high permeability for Example : Steel.
Chapter 8 Numerical Questions
Question 1.
The magnetic moment of a bar magnet is 200 A-m2 . It is free to rotate in a uniform magnetic field of 0.86 T. Find out the necessary torque in rotating the magnet slowly from a direction parallel to the field to a direction 60° from the field.
Solution:
Given : Magnetic moment M = 200A-m2
Magnetic field B = 0.86T
and Angle = θ = 60°
Necessary magnetic moment
τ = 200 × 0.86 × sin 60°
τ = 200 × 0.86 ×
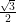
τ =

N-m
Question 2.
At any place the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is BH = 0.5 × 10-4wb/m2 and angle of dip is 45°. What will be the vertical component?
Solution:
Given : Horizontal component of earth’s magnetism
BH = 0.5 × 10-4Wb/m2
and angle of dip θ = 45°
tanθ =

BV = BH tanθ
Vertical component BV = BH tan45°
BV = BH (∵ tan45° = 1)
BV = 0.5 × 10-4Wb/m2
Question 3.
An iron rod of 1 cm2 cross-sectional area is placed in a magnetising field of 200 oersted. Then a magnetic field 300 G is produced. Calculate permeability and magnetic susceptibility of the rod.
Solution:
Given : Cross-sectional area A = 1cm2
Magnetising field H = 200 oersted
Produced magnetic field B = 3000G
Permeability μ =

= 15
and μ = (1 + Xm
15 = (1 + Xm)
Magnetic susceptibility Xm = 15 – 1 = 14
Question 4.
For a sample of iron, the relation is μ =
![\left[\frac{0.4}{H}+12 \times 10^{4}\right] \left[\frac{0.4}{H}+12 \times 10^{4}\right]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Cleft%5B%5Cfrac%7B0.4%7D%7BH%7D%2B12+%5Ctimes+10%5E%7B4%7D%5Cright%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=000&s=0)
H/m. Find out the value of H, which produce a magnetic field of 1T.
Solution:
We know that
Question 5.
Magnetising field of 2 × 103A/m produce a magnetic field of 8πT in a iron rod. Calculate relative permeability of rod.
Solution:
Magnetising field H = 2 × 103 A/m
Magnetic field B = 8πT
∵ B = μH
∴ B = μ0μrH
So, relative permeability
Question 6.
A magnetic substance of volume 30 cm3 is placed in a magnetising field of 5 oersted. It produces a magnetic moment of 6 A/m2 . Calculate the magnetic induction.
Solution:
Volume of magnetic substance V = 30cm3 = 30 × 10-6 m33 .
Magnetising field H = 5 oersted
Magnetic moment M = 6 A/m2
Question 7.
The mass of a sample of ferromagnetic substance is 0.6 kg, density is 7.8 × 103kg/m3. If the area of hysteresis loop is 0.722 m2 in an alternating magnetic field, then find out hysteresis loss per second.
Solution:
Mass of ferromagnetic sample m = 0.6kg
Density d = 7.8 × 103 kg/m3
Frequency f = 50Hz
Area of hysteresis loop A = 0.722 m3
Question 8.
The Curie temperature for a ferromagnetic substance is 300 K. If magnetic susceptibility of the substance is 0.6 at 450 K temperature, then find out Curie constant.
Solution:
Curie temperature TC = 300 K
Temperature T = 450K
Magnetic susceptibility Xm = 0.6
Question 9.
Magnetic susceptibility of a diamagnetic substance at temperature 120 K is 0.60. Find its magnetic susceptibility at 27°C.
Solution:
From Curie law
Question 10.
An iron rod of 4 cm2 cross-sectional area is parallel to a magnetising field of 103 A/m. If the magnetic flux passing through it is 4 × 10-4 Wb, then find out permeability, relative permeability and magnetic susceptibility of the substance.
Solution:
A = 4cm2 = 4 × 10-4 m2
Magnetising field H = 103A/ m
Magnetic flux ϕ = 4 × 10-4 Wb
ϕ = BA
magnetic susceptibility
Xm = μr – 1
= 796.17 – 1
= 795.17 ≈ 795
Question 11.
The radius of a circular coil is 0.05 m and number of turns are 100. If 0.1 A current is flowing through it, then how much work will be done to rotate it 180° against the perpendicular external magnetic field of 1.5 T? Initially the plane of coil is perpendicular to magnetic field.
Solution:
Given, r = 0.05 m; M = 100; I = 0.1 A;
B = 1.5T; θ1 = 0°; θ2 =180°
Work done W = – MB (cosθ2 – cosθ1)
= -NIAB(cosθ2 – cosθ1)
= -NIπr2B(cosθ2 – cosθ1)
= -100 × 0.1 × 3.14 × (0.05)2 × 1.5 × (cos180°- cos 0°)
= 2 × 100 × 0.1 × 3.14 × (0.05)2 × 1.5
= 0.236 J
Question 12.
A coil of length l is in the shape of an equilateral triangle and it is free to rotate in a magnetic field B.
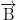
is in plane of coil. If I current is flowing through coil and it produces a torque τ, then find out side of the triangle.
Solution:
As θ = 90°










with the horizontal direction in the magnetic meridian is called angle of dip at any place. The angle of dip is different at different places on the surface of the earth. The angle between the horizontal and the final direction of the dip needle gives the angle of dip at that given location.

























0 Comments