RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Miscellaneous Exercise.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Ex 5.3 solution. Solution is provided in this post. Here we have provide the solutions of RBSE Boards Books according to chapter wise.
 |
| Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Miscellaneous Exercise |
RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Miscellaneous Exercise.
Question 1.
The common difference of two A.P.’s are same. First term of one such in 8 and of other is 3. Then difference between their 30th terms :
(A) 11
(B) 3
(C) 8
(D) 8
Solution :
30th term of first A.P.
a30 = 8 + (30 – 1)d
= 8 + 29d
30th term of second A.P.
a’30 = 3 + (30 – 1)d
= 3 + 29d
a30 – a’30 = 5
Hence, option (D) is correct.
The common difference of two A.P.’s are same. First term of one such in 8 and of other is 3. Then difference between their 30th terms :
(A) 11
(B) 3
(C) 8
(D) 8
Solution :
30th term of first A.P.
a30 = 8 + (30 – 1)d
= 8 + 29d
30th term of second A.P.
a’30 = 3 + (30 – 1)d
= 3 + 29d
a30 – a’30 = 5
Hence, option (D) is correct.
Question 2.
If 18, a, b, -3 are in A.P. then a + b =
(A) 19
(B) 7
(C) 11
(D) 15
Solution :
First term = 18
Second term 18 + d = a
Third term 18 + 2d = b
Fourth term 18 + 3d = -3
⇒ 3d = -3 – 18
⇒ 3d = -21
⇒ d = = -7
= -7
∴ Second term a = 18 + (-7) = 11
Third term b = 18 + 2 × (-7)
= 18 – 14 = 4
Thus, a + b = 11 + 4 = 15
Hence option (D) is correct
If 18, a, b, -3 are in A.P. then a + b =
(A) 19
(B) 7
(C) 11
(D) 15
Solution :
First term = 18
Second term 18 + d = a
Third term 18 + 2d = b
Fourth term 18 + 3d = -3
⇒ 3d = -3 – 18
⇒ 3d = -21
⇒ d =
∴ Second term a = 18 + (-7) = 11
Third term b = 18 + 2 × (-7)
= 18 – 14 = 4
Thus, a + b = 11 + 4 = 15
Hence option (D) is correct
Question 3.
If 7th and 13th term of A.P. are 34 and 64 respectively. Then its 18th term is :
(A) 89
(B) 88
(C) 87
(D) 90
Solution :
a7 = 34 (given)
a13 = 64 (given)
– 6d = -30
d = 5
put the value of d in a + 6d = 34
a + 6 × 5 = 34
a = 34 – 30
a = 4
∴ a18 = a + 17d
= 4 + 17 × 5 = 4 + 85 = 89
Thus, option (A) is correct.
If 7th and 13th term of A.P. are 34 and 64 respectively. Then its 18th term is :
(A) 89
(B) 88
(C) 87
(D) 90
Solution :
a7 = 34 (given)
a13 = 64 (given)
– 6d = -30
d = 5
put the value of d in a + 6d = 34
a + 6 × 5 = 34
a = 34 – 30
a = 4
∴ a18 = a + 17d
= 4 + 17 × 5 = 4 + 85 = 89
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Question 4.
First and last term of A.P. are 2 and 34 respectively. Sum of its terms is 90 then value of n will be :
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 6
Solution :
We have a = 2, l = 34, d = 8, Sn = 90
⇒ Sn = (a + l)
(a + l)
⇒ 90 = (a + l)
(a + l)
⇒ × 36 = 90
× 36 = 90
⇒ n × 18 = 90
⇒ n = = 5
= 5
⇒ n = 5
Hence, option (C) is correct.
First and last term of A.P. are 2 and 34 respectively. Sum of its terms is 90 then value of n will be :
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 6
Solution :
We have a = 2, l = 34, d = 8, Sn = 90
⇒ Sn =
⇒ 90 =
⇒
⇒ n × 18 = 90
⇒ n =
⇒ n = 5
Hence, option (C) is correct.
Question 5.
If sum of n terms of A.P. is 3n2 + 5n, then its which term is 164 :
(A) 12th
(B) 15th
(C) 27th
(D) 20th
Solution :
Given : Sn = 3n2 + 5n
S1 = 3(1)2 + 5(1) = 8
S2 = 3(2)2 + 5(2) = 22
S3 = 3(3)2 + 5(3) = 42
S4 = 3(4)2 + 5(4) = 68
∴ a1 = S1 = 8
a2 = S2 – S1 ⇒ 22 – 8 ⇒ 14
a3 = S2 – S1 ⇒ 22 – 8 ⇒ 14
a4 = S2 – S1 ⇒ 22 – 8 ⇒ 14
Thus A.P. will be 8, 14, 20, 26 …… 164
a = 8,
d = 14 – 8 = 6 and an = 164
∴ 164 = a + (n – 1)d
164 = 8 + (n – 1)
(n – 1) = 156/6 = 26
∴ n = 26 + 1 = 27
Hence, option (C) is correct.
If sum of n terms of A.P. is 3n2 + 5n, then its which term is 164 :
(A) 12th
(B) 15th
(C) 27th
(D) 20th
Solution :
Given : Sn = 3n2 + 5n
S1 = 3(1)2 + 5(1) = 8
S2 = 3(2)2 + 5(2) = 22
S3 = 3(3)2 + 5(3) = 42
S4 = 3(4)2 + 5(4) = 68
∴ a1 = S1 = 8
a2 = S2 – S1 ⇒ 22 – 8 ⇒ 14
a3 = S2 – S1 ⇒ 22 – 8 ⇒ 14
a4 = S2 – S1 ⇒ 22 – 8 ⇒ 14
Thus A.P. will be 8, 14, 20, 26 …… 164
a = 8,
d = 14 – 8 = 6 and an = 164
∴ 164 = a + (n – 1)d
164 = 8 + (n – 1)
(n – 1) = 156/6 = 26
∴ n = 26 + 1 = 27
Hence, option (C) is correct.
Question 6.
If sum of n terms of A.P. is Sn and S2n = 3Sn, then S3n : Sn will be :
(A) 10
(B) 11
(C) 6
(D) 4
Solution :
S2n = 3 Sn
 [2a + (2n – 1)d] =
[2a + (2n – 1)d] =  [2a + (n – 1)d]
[2a + (n – 1)d]
⇒ 4a + 4nd – 2d = 6a + 3nd – 3d
⇒ nd + d = 2a
Now, S3n : Sn

Hence, option (C) is correct.
If sum of n terms of A.P. is Sn and S2n = 3Sn, then S3n : Sn will be :
(A) 10
(B) 11
(C) 6
(D) 4
Solution :
S2n = 3 Sn
⇒ 4a + 4nd – 2d = 6a + 3nd – 3d
⇒ nd + d = 2a
Now, S3n : Sn

Hence, option (C) is correct.
Question 7.
The first and last terms of an A.P. are 1 and 11 respectively. If sum of its terms is 36 then number of terms will be :
(A) 5
(B) 6
(C) 9
(D) 11
Solution :
a= 1, l = 11, Sn = 36
Sn = (a + l)
(a + l)
36 = (1 + 11)
(1 + 11)
⇒ 36 = × 12
× 12
⇒ 36 = 6n
⇒ n = 6
Hence, option. (B) is correct.
The first and last terms of an A.P. are 1 and 11 respectively. If sum of its terms is 36 then number of terms will be :
(A) 5
(B) 6
(C) 9
(D) 11
Solution :
a= 1, l = 11, Sn = 36
Sn =
36 =
⇒ 36 =
⇒ 36 = 6n
⇒ n = 6
Hence, option. (B) is correct.
Question 8.
Write 5th term of A.P. 3, 5, 7, 9, …., 201 from last.
Solution :
Given A.P.
3, 5, 7, 9 …… 201
First term (a) = 3
Common difference (d) = 5 – 3 = 2
Last term (an) = 201
Formula : rth term from last = an – (r – 1)d
5th term from last = 201 – (5 – 1)2
= 201 – 4 × 2
= 201 – 8
= 193
Hence, 5th term from last 193.
Write 5th term of A.P. 3, 5, 7, 9, …., 201 from last.
Solution :
Given A.P.
3, 5, 7, 9 …… 201
First term (a) = 3
Common difference (d) = 5 – 3 = 2
Last term (an) = 201
Formula : rth term from last = an – (r – 1)d
5th term from last = 201 – (5 – 1)2
= 201 – 4 × 2
= 201 – 8
= 193
Hence, 5th term from last 193.
Question 9.
If three consecutive terms of A.P. are , a, 2, then find.
, a, 2, then find.
Solution :
Given A.P. , a, 2
, a, 2
First term =
Second term a = + d
+ d
Third term 2 = + 2d
+ 2d
⇒ 2 – = 2d
= 2d
⇒ = 2d
= 2d
⇒ = 2d
= 2d
⇒ 2d =
⇒ d =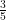
Second term a = + d
+ d
= +
+ 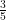 =
= 
Thus, a =
If three consecutive terms of A.P. are
Solution :
Given A.P.
First term =
Second term a =
Third term 2 =
⇒ 2 –
⇒
⇒
⇒ 2d =
⇒ d =
Second term a =
=
Thus, a =
Question 10.
Find the sum of first 1000 positive integers.
Solution :
Given A.P.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5 …….. 1000
First term (a) = 1
Common difference (d) = 2 – 1 = 1
Last term (l) = 1000
Formula, Sn = (a + l)
(a + l)
S1000 = (1 + 1000)
(1 + 1000)
= 500 × 1001 = 500500
Hence, sum of first 1000 positive integers.
= 500500
Find the sum of first 1000 positive integers.
Solution :
Given A.P.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5 …….. 1000
First term (a) = 1
Common difference (d) = 2 – 1 = 1
Last term (l) = 1000
Formula, Sn =
S1000 =
= 500 × 1001 = 500500
Hence, sum of first 1000 positive integers.
= 500500
Question 11.
Is any term of sequence 5, 11, 17, 23, …. will be 299 ?
Solution :
Given A.P.
5, 11, 17, 23, ……..
First term (a) = 5
Common difference (d) = 11 – 5 = 6
nth term (an) = 299
Formula an = a + (n – 1)d
⇒ 299 = 5 + (n – 1) × 6
⇒ 299 – 5 = (n – 1) 6
⇒ 294 = (n – 1) 6
⇒ n – 1 =
⇒ n – 1 = 49
⇒ n = 49 + 1
⇒ n = 50
n is whole no.
∴ Hence, 299 is 50th term of sequence 5, 11, 17, 23 ….
Is any term of sequence 5, 11, 17, 23, …. will be 299 ?
Solution :
Given A.P.
5, 11, 17, 23, ……..
First term (a) = 5
Common difference (d) = 11 – 5 = 6
nth term (an) = 299
Formula an = a + (n – 1)d
⇒ 299 = 5 + (n – 1) × 6
⇒ 299 – 5 = (n – 1) 6
⇒ 294 = (n – 1) 6
⇒ n – 1 =
⇒ n – 1 = 49
⇒ n = 49 + 1
⇒ n = 50
n is whole no.
∴ Hence, 299 is 50th term of sequence 5, 11, 17, 23 ….
Question 12.
Which term of AP. 20, 19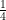 , 18
, 18  , 17
, 17 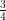 ,… is first negative term.
,… is first negative term.
Solution :
Given series is A.P. whose
First term (a) = 20 and common difference
(d) = – 3/4
∴ Let the nth term of the given AP the first negative term then
an < 0
⇒ a + (n – 1)d < O
⇒ 20 + (n – 1) × –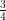 < 0
< 0
⇒ –
–  < 0
< 0
⇒ 83 – 3n < 0 ⇒ 3n > 83
⇒ n > 27 ⇒ n ≥ 28
⇒ n ≥ 28
Thus, 29th term of the given sequence the first negative term.
Which term of AP. 20, 19
Solution :
Given series is A.P. whose
First term (a) = 20 and common difference
(d) = – 3/4
∴ Let the nth term of the given AP the first negative term then
an < 0
⇒ a + (n – 1)d < O
⇒ 20 + (n – 1) × –
⇒
⇒ 83 – 3n < 0 ⇒ 3n > 83
⇒ n > 27
Thus, 29th term of the given sequence the first negative term.
Question 13.
Four numbers are in A.P. If their sum is 20 and sum of their squares is 120, then find the numbers.
Solution :
Let in four numbers,
First number = a – 3d
Second number = a – d
Third number = a + d
Fourth number = a + 3d
Sum of four number is 20
∴ 20 = (a – 3d) + (a – d) + (a + d) + (a + 3d)
⇒ 20 = 4a
⇒ a = 5
Sum of squares of four numbers is 120.
∴ (a – 3d)2 + (a – d)2 + (a + d)2 + (a + 3d)2 = 120
⇒ [a2 + 9d2 – 6ad + a2 + d2 – 2ad + a2 + d2 + 2ad + a2 + 9d2 + 6ad] = 120
⇒ 4 (a2 + 5d2) = 120
⇒ a2 + 5d2 = 30 [∵ a = 5]
⇒ 52 + 5d2 = 30
⇒ 25 + 5d2 = 30
⇒ 5d2 = 30 – 25
⇒ 5d2 = 5
⇒ d2 = 1
⇒ d = ±1
Thus, a = 5 and d = ± 1
∴ Four numbers are 2, 4, 6, 8 or 8, 6, 4, 2
Four numbers are in A.P. If their sum is 20 and sum of their squares is 120, then find the numbers.
Solution :
Let in four numbers,
First number = a – 3d
Second number = a – d
Third number = a + d
Fourth number = a + 3d
Sum of four number is 20
∴ 20 = (a – 3d) + (a – d) + (a + d) + (a + 3d)
⇒ 20 = 4a
⇒ a = 5
Sum of squares of four numbers is 120.
∴ (a – 3d)2 + (a – d)2 + (a + d)2 + (a + 3d)2 = 120
⇒ [a2 + 9d2 – 6ad + a2 + d2 – 2ad + a2 + d2 + 2ad + a2 + 9d2 + 6ad] = 120
⇒ 4 (a2 + 5d2) = 120
⇒ a2 + 5d2 = 30 [∵ a = 5]
⇒ 52 + 5d2 = 30
⇒ 25 + 5d2 = 30
⇒ 5d2 = 30 – 25
⇒ 5d2 = 5
⇒ d2 = 1
⇒ d = ±1
Thus, a = 5 and d = ± 1
∴ Four numbers are 2, 4, 6, 8 or 8, 6, 4, 2
Question 14.
If sum of n terms of A.P. is then find its 25th term.
then find its 25th term.
Solution :
Given that, sum of n terms of A.P.
Sn =

Hence 25th term will be 76.
If sum of n terms of A.P. is
Solution :
Given that, sum of n terms of A.P.
Sn =

Hence 25th term will be 76.
 |
| Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Miscellaneous Exercise |
Question 15.
The houses of a row are numbered consecutively from 1 to 49. Show that there is value of x such that the sum of the numbers of the houses preceding the house numbered x is equal to the sum of the houses following it. Find the value of x.
Solution :
Consecutively marked number of houses are 1, 2, 3, 4 …… 47, 48, 49.
x is such number so that sum of one side of x numbers = sum of other side number of x d in all the terms of series = 1.
then sum of number from 1 to x – 1, (a) = 12, n = x – 1.

and sum of numbers from x + 1 to 49

Then according to question,

Hence, value of x is 35.
The houses of a row are numbered consecutively from 1 to 49. Show that there is value of x such that the sum of the numbers of the houses preceding the house numbered x is equal to the sum of the houses following it. Find the value of x.
Solution :
Consecutively marked number of houses are 1, 2, 3, 4 …… 47, 48, 49.
x is such number so that sum of one side of x numbers = sum of other side number of x d in all the terms of series = 1.
then sum of number from 1 to x – 1, (a) = 12, n = x – 1.

and sum of numbers from x + 1 to 49

Then according to question,

Hence, value of x is 35.
Hope that the Solutions provided here for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Miscellaneous Exercise will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Miscellaneous Exercise solution drop a comment below and like and share the post.
Thank you.






0 Comments