Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 Similarity Ex 11.3
Question 1.
In two triangles ABC and PQR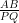 =
=  . For similarity of two triangles which angles should be equal, name them and also given reason for your answer.
. For similarity of two triangles which angles should be equal, name them and also given reason for your answer.
Solution :
In ∆ABC and ∆PQR,
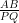 =
= 
⇒ =
= 

Angle formed by sides AB and BC is ∠B
Angle formed by sides PQ and QR is ∠Q
∴ ∠B = ∠Q is essential for similarity of two triangles.
thus ∠B = ∠Q
 =
= 
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆PQR (SAS similarity theorem)
In two triangles ABC and PQR
Solution :
In ∆ABC and ∆PQR,
⇒

Angle formed by sides AB and BC is ∠B
Angle formed by sides PQ and QR is ∠Q
∴ ∠B = ∠Q is essential for similarity of two triangles.
thus ∠B = ∠Q
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆PQR (SAS similarity theorem)
Question 2.
In ∆ABC and ∆DEF; ∠A = ∠D, ∠B = ∠F. Is ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF ? Given reason for your answer.
Solution :
No, because when ∠A = ∠D, ∠B = ∠F, then ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF.
In ∆ABC and ∆DEF; ∠A = ∠D, ∠B = ∠F. Is ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF ? Given reason for your answer.
Solution :
No, because when ∠A = ∠D, ∠B = ∠F, then ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF.
Question 3.
If ∆ABC ~ ∆FDE then is it possible?
 =
=  =
=  Give reason for your answer.
Give reason for your answer.
Solution :
∆ABC ~ ∆FDE (Given)
∴ ∠A = ∠F, ∠B = ∠D and ∠C = ∠E
Side AB ↔ FD, Side BC ↔ DE, side AC ↔ FE
∴ =
=  =
= 
Thus =
=  =
= 
is not possible.
If ∆ABC ~ ∆FDE then is it possible?
Solution :
∆ABC ~ ∆FDE (Given)
∴ ∠A = ∠F, ∠B = ∠D and ∠C = ∠E
Side AB ↔ FD, Side BC ↔ DE, side AC ↔ FE
∴
Thus
is not possible.
Question 4.
If two sides and one angle of a triangle are proportional and equal to two sides and one angle of other triangle respectively then two triangle are similar. Is this true ? Give answer with reason.
Solution :
This statement is false because for similarity of triangles two sides and angle included them should be equal.
If two sides and one angle of a triangle are proportional and equal to two sides and one angle of other triangle respectively then two triangle are similar. Is this true ? Give answer with reason.
Solution :
This statement is false because for similarity of triangles two sides and angle included them should be equal.
Question 5.
What do you mean by equiangular triangles ? What relation can be between them?
Solution :
If corresponding angles of two equiangular triangles are same, then both triangles will be similar.

In ∆ABC and ∆DEF
∠A = ∠D
∠B = ∠E
and ∠C = ∠F
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF
What do you mean by equiangular triangles ? What relation can be between them?
Solution :
If corresponding angles of two equiangular triangles are same, then both triangles will be similar.

In ∆ABC and ∆DEF
∠A = ∠D
∠B = ∠E
and ∠C = ∠F
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF
Question 6.
From the following figures of triangles, select the similar pair and write in notation form of similarity.


Solution :
(i) In ∆ABC and ∆PQR

∠A = ∠Q = 40°
∠B = ∠P = 60°
∠C = ∠R = 80°
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆QPR
Thus figure (i) and (viii) will be similar.
From the following figures of triangles, select the similar pair and write in notation form of similarity.


Solution :
(i) In ∆ABC and ∆PQR

∠A = ∠Q = 40°
∠B = ∠P = 60°
∠C = ∠R = 80°
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆QPR
Thus figure (i) and (viii) will be similar.
(ii) In ∆MNP and ∆XYZ

∠M = ∠Z = 70°
∠P = ∠Y = 30°
∴ ∆MNP ~ ∆XYZ
Thus, figure (ii) and (vii) will be similar.
(iii) In ∆PQR and ∆EFG

∴ ∆PQR and ∆EFG are similar
The figure (iii) and (v) will be similar.
(iv) ∆EFG and ∆LMN

∴ ∆MLN ~ ∆EFG are similar
Hence figure (iv) and (vi) are similar.

∠M = ∠Z = 70°
∠P = ∠Y = 30°
∴ ∆MNP ~ ∆XYZ
Thus, figure (ii) and (vii) will be similar.
(iii) In ∆PQR and ∆EFG

∴ ∆PQR and ∆EFG are similar
The figure (iii) and (v) will be similar.
(iv) ∆EFG and ∆LMN

∴ ∆MLN ~ ∆EFG are similar
Hence figure (iv) and (vi) are similar.
Question 7.
In figure, ∆PQR ~ ∆TRS then find in this similar pair which angles should be equal ?

Solution :
∆PQR ~ ∆TRS
∴ ∠R = ∠R (common angle)
∠P = ∠RTS (corresponding angle)
∠Q = ∠RST (corresponding angle)
Thus, above angle should be same for similar triangle pair.
In figure, ∆PQR ~ ∆TRS then find in this similar pair which angles should be equal ?

Solution :
∆PQR ~ ∆TRS
∴ ∠R = ∠R (common angle)
∠P = ∠RTS (corresponding angle)
∠Q = ∠RST (corresponding angle)
Thus, above angle should be same for similar triangle pair.
Question 8.
You have to select two triangle in figures which are similar to each other. If ∠CBE = ∠CAD.

Solution :
In ∆CAD and ∆CBE

∠ACD = ∠BCE (common angle)
∠CAD = ∠CBE (given)
∴ ∆CAD ~ ∆CBE (AA similarity law)
Hence, ∆ADC ~ ∆BEC
You have to select two triangle in figures which are similar to each other. If ∠CBE = ∠CAD.

Solution :
In ∆CAD and ∆CBE

∠ACD = ∠BCE (common angle)
∠CAD = ∠CBE (given)
∴ ∆CAD ~ ∆CBE (AA similarity law)
Hence, ∆ADC ~ ∆BEC
Question 9.
In fig. PQ and RS are parallel then prove that : ∆POQ ~ ∆SOR.

Solution :
In ∆POQ and ∆SOR
PQ || RS (given)
∠OPQ = ∠OSR (Alternate angle)
∠POQ = ∠ROS (Vertically opposite angles)
and ∠OQP = ∠ORS (Alternate angles)

By AAA similarity law
∴ ∆POQ ~ ∆SOR
In fig. PQ and RS are parallel then prove that : ∆POQ ~ ∆SOR.

Solution :
In ∆POQ and ∆SOR
PQ || RS (given)
∠OPQ = ∠OSR (Alternate angle)
∠POQ = ∠ROS (Vertically opposite angles)
and ∠OQP = ∠ORS (Alternate angles)

By AAA similarity law
∴ ∆POQ ~ ∆SOR
Question 10.
A girl with height 90 cm walks away from the base of lamp-post at a speed of 1.2 m/sec. lithe lamp is 3.6 m above the ground. Find the length of her shadow after 4 seconds.
Solution :
Let AB = Lamp post
CD = girl
DE = shadow of the girl,
BD = 1.2 × 4 = 4.8 m

Let shadow of girl,
DE = ‘a’ m
In ∆ABE and ∆CDE
∠B = ∆(each 90°)
∠E = ∠E (comman angle)
∆ABE ~ ∆CDE by (AA criterion)
therefore, =
=  ⇒
⇒  =
= 
⇒ 4.8 + a = 4a
⇒ 3 a = 4.8
⇒ a = 1.6 m
Thus after 4 sec. length of girl’s shadow will be 1.6 m
A girl with height 90 cm walks away from the base of lamp-post at a speed of 1.2 m/sec. lithe lamp is 3.6 m above the ground. Find the length of her shadow after 4 seconds.
Solution :
Let AB = Lamp post
CD = girl
DE = shadow of the girl,
BD = 1.2 × 4 = 4.8 m

Let shadow of girl,
DE = ‘a’ m
In ∆ABE and ∆CDE
∠B = ∆(each 90°)
∠E = ∠E (comman angle)
∆ABE ~ ∆CDE by (AA criterion)
therefore,
⇒ 4.8 + a = 4a
⇒ 3 a = 4.8
⇒ a = 1.6 m
Thus after 4 sec. length of girl’s shadow will be 1.6 m
Question 11.
The shadow of a vertical pillar of height 12 m is 8 m. At the same time length of shadow 12 m is 8 m. At the same time length of shadow of tower is 56 m then find height of tower.
Solution :
In the figure Length of a vertical pillar AB = 12 m
Length of shadow BC = 8 m
At the same time QC is shadow of other tower PQ.

Here, QC = 56 m
Now, In ∆ABC and ∆PQC
∠B = ∠Q = 90°
∠C = ∠C (Common angle)
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆PQC
By similarity rule
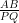 =
= 
 =
= 
PQ = = 84 m
= 84 m
Thus, height of tower PQ = 84 m
The shadow of a vertical pillar of height 12 m is 8 m. At the same time length of shadow 12 m is 8 m. At the same time length of shadow of tower is 56 m then find height of tower.
Solution :
In the figure Length of a vertical pillar AB = 12 m
Length of shadow BC = 8 m
At the same time QC is shadow of other tower PQ.

Here, QC = 56 m
Now, In ∆ABC and ∆PQC
∠B = ∠Q = 90°
∠C = ∠C (Common angle)
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆PQC
By similarity rule
PQ =
Thus, height of tower PQ = 84 m
Question 12.
From vertex A of ∆ABC a perpendicular is drawn on opposite side BC and get AD2 = BD × DC, then show that ABC is a right angled triangle.
Solution :
Given : Perpendicular from vertex A of ∆ABC to side BC.

AD ⊥ BC
AD2 = BD × DC

From vertex A of ∆ABC a perpendicular is drawn on opposite side BC and get AD2 = BD × DC, then show that ABC is a right angled triangle.
Solution :
Given : Perpendicular from vertex A of ∆ABC to side BC.

AD ⊥ BC
AD2 = BD × DC

Question 13.
By joining mid-point of three sides of a triangle, four triangle so formed are similar to original triangle.
Solution :
Given : D, E, F are mid-point of sides AB, BC and BC of ΔABC.
To prove: ∆ADE ~ ∆DBF ~ ∆EFC ~ ∆DEF ~ ∆ABC
Four triangle formed in figure are similar to original ∆ABC

Proof : Points D and E are mid-point of sides AB and AC.
∴ DE = BC and DE || BC (by mid-point theorem) …(i)
BC and DE || BC (by mid-point theorem) …(i)
E and F are mid-point of AC and BC sides.
∴ EF = AB and EF || AB …(ii)
AB and EF || AB …(ii)
Point F and D are mid-point of sector BC and AB.
∴ FD = AC and FD || AC …(iii)
AC and FD || AC …(iii)
From eqn (i) and (ii)
DE || BC and EF || AB
∴ DEFB is a parallelogram
Diagonal of ||gm DEFB, DE divides into two congruent triangles.
∴ ∆DBF = ∆DEF …(iv)
Similarly, diagonal EF, divides the ||gm DECF into two congrwnent triangles.
∴ ∆DEF = ∆DAE …(v)
Simlarly, diagonal EF, divides the ||gm DECF into two congruemt triangles.
∴ ∆DEF = ∆EFC …(iv)
From (iv), (v) and (vi)
∴ ∆DEF = ∆DAE = ∆EFC = ∆DBF
∵ DE || BC
∠C = ∠E
∴ ∠B = ∠D (corresponding angle)
⇒ ∆ABC ~ ∆ADE
Thus, ∆ABC ~ ∆ADE ~ ∆BDF ~ ∆EFC
By joining mid-point of three sides of a triangle, four triangle so formed are similar to original triangle.
Solution :
Given : D, E, F are mid-point of sides AB, BC and BC of ΔABC.
To prove: ∆ADE ~ ∆DBF ~ ∆EFC ~ ∆DEF ~ ∆ABC
Four triangle formed in figure are similar to original ∆ABC

Proof : Points D and E are mid-point of sides AB and AC.
∴ DE =
E and F are mid-point of AC and BC sides.
∴ EF =
Point F and D are mid-point of sector BC and AB.
∴ FD =
From eqn (i) and (ii)
DE || BC and EF || AB
∴ DEFB is a parallelogram
Diagonal of ||gm DEFB, DE divides into two congruent triangles.
∴ ∆DBF = ∆DEF …(iv)
Similarly, diagonal EF, divides the ||gm DECF into two congrwnent triangles.
∴ ∆DEF = ∆DAE …(v)
Simlarly, diagonal EF, divides the ||gm DECF into two congruemt triangles.
∴ ∆DEF = ∆EFC …(iv)
From (iv), (v) and (vi)
∴ ∆DEF = ∆DAE = ∆EFC = ∆DBF
∵ DE || BC
∠C = ∠E
∴ ∠B = ∠D (corresponding angle)
⇒ ∆ABC ~ ∆ADE
Thus, ∆ABC ~ ∆ADE ~ ∆BDF ~ ∆EFC
Question 14.
According to following figure, If AB ⊥ BC, DC ⊥ BC and DE ⊥ AC then prove that ∆CED ~ ∆ABC

Solution :
Given
AB ⊥ BC, DC ⊥ BC and DE ⊥ AC
To prove : ∆CED ~ ∆ABC
Proof : AB ⊥ BC and DC ⊥ BC
∴ AB || DC
When AB || DC cuts by transversal AC
∠BAC = ∠ACD
or ∠BAC = ∠ECD
∠B = ∠E = 90° (given) …(ii)
∴ ∠ACB = ∠EDC [due to (i) and (ii)]
⇒ ∆ABC ~ ∆CED.
According to following figure, If AB ⊥ BC, DC ⊥ BC and DE ⊥ AC then prove that ∆CED ~ ∆ABC

Solution :
Given
AB ⊥ BC, DC ⊥ BC and DE ⊥ AC
To prove : ∆CED ~ ∆ABC
Proof : AB ⊥ BC and DC ⊥ BC
∴ AB || DC
When AB || DC cuts by transversal AC
∠BAC = ∠ACD
or ∠BAC = ∠ECD
∠B = ∠E = 90° (given) …(ii)
∴ ∠ACB = ∠EDC [due to (i) and (ii)]
⇒ ∆ABC ~ ∆CED.
Question 15.
D is mid-point of side BC of ∆ABC. A line is drawn through B and bisects AD at point E and A at C, then prove that =
= 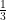
Solution :
Given : D is mid-point of side BC of ∆ABC.

BD = DC
and AE = ED
To prove:
 =
= 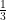
Construction : Draw DY || BX meeting AC at Y
Proof : In ∆BCX and ∆DCY
∠BCX = ∠DCY (common)
∠BXC = ∠DYC (corresponding angle)
So, ∆BCX ~ ∆DCY (AA similarity)

D is mid-point of side BC of ∆ABC. A line is drawn through B and bisects AD at point E and A at C, then prove that
Solution :
Given : D is mid-point of side BC of ∆ABC.

BD = DC
and AE = ED
To prove:
Construction : Draw DY || BX meeting AC at Y
Proof : In ∆BCX and ∆DCY
∠BCX = ∠DCY (common)
∠BXC = ∠DYC (corresponding angle)
So, ∆BCX ~ ∆DCY (AA similarity)







0 Comments