RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 Constructions
Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 Constructions Ex 14.1 Solution is provided in this post . Here we have provide the solutions of RBSE Boards Books according to chapter wise.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 Constructions Ex 14.1
Question 1.
Divide a line segment of length 6.7 cm in the ratio of 2 : 3.
Solution :
Given :
Line segment AB = 6.7 cm
Steps of construction : (1) Draw a line segment AB = 6.7 cm.
(2) Draw a ray AX, making an acute angle with AB.
(3) Locate 5(2 + 3) point A1, A2, A3, A4 and A5 on AX so that AA1 = A1A2 = A2A3 = A3A4 = A4A5.

(4) Join BA5.
(5) Through the point A2. draw a line parallel to BA5 (By making an angle equal to ∠AA5B) that intersects AB at point P.
then AP : PB = 2 : 3
Verification: In ΔABA5 PA2 || BA5.
∴ ΔAPA2 ~ ΔABA5
⇒  =
=  =
= 
⇒ AP : PB = 2 : 3.
Question 2.
Draw a line segment AB = 8.3 cm. Find a point C on AB such that AC = 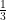 AB. Also prove it.
AB. Also prove it.
Solution :
Steps of construction :
(1) Draw a line segment AB = 8.3 cm
(2) Make an acute angle BAX on AB.
(3) Taking any of this distance mark three arcs A1, A2 and A3, such that
AA1 = A1A2 = A2A3

(4) Join A3B
(5) Draw a line from A1, parallel to A3B, that join AB at point C.
(6) C is such tha point on AB that
AC = 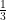 AB
AB
Verification : In ΔABA3

⇒ 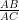 =
=  =
= 
⇒  =
= 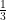
AC = 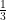 AB
AB
Hence, C is the point on AB such that AC = 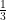 AB Hence proved
AB Hence proved
Question 3.
Draw a tangent to a circle at point P with radius 2.8 cm.
Solution :
Steps of construction:
(1) Draw a circle with center O and radius 2.8 cm.
(2) Take a point P on the circumference of the circle and join O to P.
(3) Draw a perpendicular at P of OP i.e., make an angle OPA 90°. Produce AP to B

APB in the required tangent.
Question 4.
Draw two tangents to two ends of diameter of a circle with center O and radius 3 cm. If the tangents drawn will ever Intersect each other. Give a suitable reason in the support of your answer.
Solution :
Steps of construction :
(1) Draw a circle with center O and radius 3 cm.

(2) Draw PQ, diameter of the circle.
(3) Draw a PA at point P of OP thus ∠OPA = 90°. Produce AP to B. APB is a tangent to the circle at point P.
(4) Similarly, draw a tangent A’QB’ at Q of OQ.
Hence AOB and A’QB’ are the required tangents.
Since, two tangents are parallel to each other So they will never intersect each other.
Question 5.
Take a chord of length 2.3 cm In a circle with center O and radius 3.1 cm. Draw two tangents to two ends of this chord.
Solution :
Steps of Construction :
First of all draw a circle with center O and radius 3.1 cm.

(2) Taking a point P on the circumference of the circle as a center and radius 2.3 cm draw an arc to intersect the circle at Q. Joining PQ obtain the chord PQ.
(3) Draw perpendiculars AP and OX on OP and QQ respectively.
(4) Produce AP to B and QX to Y.
Hence AB and XY are the required tangents.
Question 6.
Construct a circle with radius 2.7 cm and draw a tangent to this circle.
Solution :
Steps of construction :
(1) Taking O as center and radius 2.7, draw a circle.
(2) Take a point P on the circle.
(3) Join OP.

(4) At point P of OP draw a ray APB to make an angle 90°.
Hence, APB is the required tangent to the given circle at point P.
Question 7.
Taking O as center and radius 2.4 cm draw a circle. Making an angle of 60 between two radii OA and OB drawn, draw two tangents at points A and B of OA and OB respectively which intersect each other at T. Measure the angle ATB.
Solution :
Given :
A circle with center O and radius OB = 2.4 cm and an angle of 60° between two radii 04 and OB of the circle.
Steps of construction :
(1) Draw a circle with radius 2.4 cm whose center is O. At center O, draw two radii OA and OB such that ∠AOB = 60°.

(2) At point B of OB draw a ray making an angle of 90°. Similarly at point A of OA draw another ray making an angle of 90°, which intersect each
other at T.
AT and BT are the required tangents measurement of ∠ATB is 120°.
Question 8.
Draw two tangents to the circle with radius O and radius 3.2 cm. Such that the measure of the angle between them is 70°.
Solution :
Given :
∠APB = 70°
and ∠A = ∠B = 90°
∴ Forth angle of quadrilateral AOBP
∠AOB = 360° – (70° + 90° + 90°)
= 360° – 250°
= 110°
Thus the angle between radii OA and OB.
= ∠AOB = 110°.
Steps of construction:
(1) Draw a circle with center O and radius 3.2 cm. Thaw an angle ∠AOB = 110° between radii OA and OB.
(2) Draw perpendicular at A and B of OA and OB respectively that meet each other at point P.

Hence, AP and BP are the required tangents.
Question 9.
Draw a circle of radius 3 cm. Construct two tangents from an external point P of 5 cm away from the center of the circle.
Solution :
Given :
A circle of radius 3 cm and a point P 5 cm away from its center.

Steps of construction :
(1) Draw a circle with center O and radius 3 cm.
(2) Take a point P at distance of 5 cm from the center of the circle.
(3) Join OP and draw its perpendicular bisector which intersects OP at M.
(4) With M as center and radius PM, draw another circle which intersects the given circle at T1 and T2.
(5) Join PT1 and PT2 are the tangents of given circle.
Question 10.
Draw two circle of radii 3 cm and 4 cm, where the distance between their centers is 8 cm. Construct direct common tangents of these circles. How many common tangents can be drawn of these circles.
Solution:
Given :
r1 = 4 cm r2 = 3 cm C1C2 = 8 cm
∵ C1C2 > r1 + r2 i.e.. 8 > (3 + 4)
Thus 4 common tangents can be drawn.
To construct : Two direct common tangents.
Steps of construction :
(1) Draw a line segment C1C2 = 8 cm.
(2) Taking C1 as centre and radius 4 cm draw a circle.
(3) Taking C2 as centre and radius 3 cm draw another circle.
(4) Draw perpendicular bisector of C1C2 which intersects C1C2 at M.

(5) Taking M as center and radius MC1 = MC2 draw another circle.
(6) Taking C1 as centre and radius 4 – 3 = 1 cm draw a circle which intersects the circle center M at P and Q.
(7) Join C1P and C1Q and produce to intersect the given circle at A and A’.
(8) From point C2 draw C1P || C2B and C1A’ || C2B’.
(9) Join AB and A’B’
Hence, AB and A’B’ are the required tangents.
Question 11.
The distance between the centers of two circles is 6 cm. Radius of one circle is 1.7 cm and that of other circle is 2.8 cm. Draw a Indirect common tangent of these circle.
Solution :
Given: r1 = 17 cm, r2 = 2.8 cm and the distance between these centers C12 = 56 cm.
To Construct : indirect (transversal) common tangent.
Steps of Construction:
(1) Draw a line segment of the length of 6 cm the distance between two centers C1C2
(2) Taking C1 as center and radius 1.7 cm draw a circle.
(3) Taking C2 as center and radius 2.8 cm draw another circle.
(4) Draw the perpendicular bisector of C1C2 which intersects it at M.
(5) Taking M as center and radius MC1 = MC2 draw another circle.
(6) Taking the radius equal to the sum of two radii center C1 the centre of smaller circle draw a circle. i.e., radius 1.7 + 2.8 = 4.5 cm and center C1 which intersects the circle with diameter C1C2 at A and B.

(7) Join AC2 and AC1 which intersect the circle radius 1.7 cm at P.
(8) Join P to Q.
Hence, PQ is the required indirect common tangent.
We hope that the material provided on this website will be helpful for you. If you have any query regarding any topic related to Rajasthan Board of Secondary education then drop a comment below we will try give you response as soon as possible. if you enjoyed the post, i'd very grateful if you would help it spread by emailing it to a friend, or sharing it on twitter or facebook. Thank you!







0 Comments