RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Ex 5.1.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Ex 5.1 solution. Solution is provided in this post. Here we have provide the solutions of RBSE Boards Books according to chapter wise.
RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Ex 5.1.
Question 1.
Find the first term and common difference for the following A.P –
(i) 6, 9, 12, 15, ….
(ii) – 7, – 9, – 11, – 13
(iii)
(iv) 1, – 2, – 5, – 8 ……
(v) -1,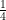 ,
, 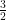 , ….
, ….
(vi) 3, 1, -1, -3, ….
(vii) 3, -2, -7, -12, …..
Solution :
(i) Given A.P. is 6, 9, 12, 15. …
First term (a1) = 6
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= 9 – 6 = 3
Thus, a1 = 6 and d = 3
Find the first term and common difference for the following A.P –
(i) 6, 9, 12, 15, ….
(ii) – 7, – 9, – 11, – 13
(iii)
(iv) 1, – 2, – 5, – 8 ……
(v) -1,
(vi) 3, 1, -1, -3, ….
(vii) 3, -2, -7, -12, …..
Solution :
(i) Given A.P. is 6, 9, 12, 15. …
First term (a1) = 6
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= 9 – 6 = 3
Thus, a1 = 6 and d = 3
(ii) Given A.P. is -7, -9, -11, -13, ……
First term (a1) = – 7
Common difference (d)
= a2 – a1
= -9 – (-7)
= -9 + 7 = -2
Thus, a1 = -7 and d = -2
(iii) Given A.P. is
First term (a1) =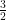
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= –
– 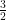
= =
= 
= -1
Thus, a1 = and d = – 1
(iv) Given A.P. is 1, -2, -5, -8, …….
First term (a1) = 1
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= -2 – (1)
= -3
Thus, a1 = 1 and d = -3
First term (a1) = – 7
Common difference (d)
= a2 – a1
= -9 – (-7)
= -9 + 7 = -2
Thus, a1 = -7 and d = -2
(iii) Given A.P. is
First term (a1) =
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
=
=
= -1
Thus, a1 = and d = – 1
(iv) Given A.P. is 1, -2, -5, -8, …….
First term (a1) = 1
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= -2 – (1)
= -3
Thus, a1 = 1 and d = -3
(v) Given A.P. -1, 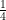 ,
, 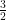 , …..
, …..
First term (a1) = – 1
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
=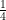 – (-1)
– (-1)
=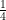 + 1
+ 1
= =
= 
Thus, a1 = -1 and d =
(vi) Given A.P. is 3, 1, -1, -3, …..
First term (a1) = 3
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= 1 – 3
Thus, a1 = 3 and d = -2
(vii) Given A.P. is 3, -2, -7, -12 , …..
First term (a1) = 3
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= -2 – 3
= -5
Thus, a1 = 3 and d = -5.
First term (a1) = – 1
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
=
=
=
Thus, a1 = -1 and d =
(vi) Given A.P. is 3, 1, -1, -3, …..
First term (a1) = 3
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= 1 – 3
Thus, a1 = 3 and d = -2
(vii) Given A.P. is 3, -2, -7, -12 , …..
First term (a1) = 3
Common difference (d) = a2 – a1
= -2 – 3
= -5
Thus, a1 = 3 and d = -5.
Question 2.
If first term a and common difference d of an AP in given as follows, then find next four terms of that series.
(i) a = -1, d =
(ii) a =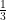 , d =
, d = 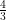
(iii) a = 0.6 , d = 1.1
(iv) a = 4, d = -3
(v) a = 11, d = -4
(vi) a = – 1.25, d = -0.25
(vii) a = 20, d =
Solution :
(i) Given a = -1, d =
First term (a) = -1
Second term (a + d) =-1 + = –
= –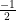
Third term (a + 2d) = -1 + 2 × = o
= o
Fourth term (a + 3d) = -1 + 3 ×
= -1 +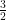
= =
= 
Thus, First four terms of A.P. are – 1, – , 0 and
, 0 and  .
.
If first term a and common difference d of an AP in given as follows, then find next four terms of that series.
(i) a = -1, d =
(ii) a =
(iii) a = 0.6 , d = 1.1
(iv) a = 4, d = -3
(v) a = 11, d = -4
(vi) a = – 1.25, d = -0.25
(vii) a = 20, d =
Solution :
(i) Given a = -1, d =
First term (a) = -1
Second term (a + d) =-1 +
Third term (a + 2d) = -1 + 2 ×
Fourth term (a + 3d) = -1 + 3 ×
= -1 +
=
Thus, First four terms of A.P. are – 1, –
(ii) Given a = 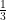 , d =
, d = 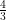
First term (a) =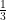

(iii) Given a = 0.6, d = 1.1
First term (a) = 0.6
Second term (a + d) = 0.6 + 1.1 = 1.7
Third terms (a + 2d) = 0.6 + 2 × 1.1 = 2.8
Fourth term (a + 3d) = 0.6 + 3 × 1.1 = 3.9
Hence, four terms of A.P are 0.6, 1.7, 2.8 and 3.9.
First term (a) =

(iii) Given a = 0.6, d = 1.1
First term (a) = 0.6
Second term (a + d) = 0.6 + 1.1 = 1.7
Third terms (a + 2d) = 0.6 + 2 × 1.1 = 2.8
Fourth term (a + 3d) = 0.6 + 3 × 1.1 = 3.9
Hence, four terms of A.P are 0.6, 1.7, 2.8 and 3.9.
(iv) Given a = 4, d = -3
First term (a) = 4
Second term (a + d) = 4 + (-3) = 1
Third term (a + 2d) = 4 + 2 (-3) = 4 – 6 = -2
Fourth term (a + 3d) = 4 + 3(-3) = 4 – 9 = -5
Hence, four terms of A.P are 4, 1, -2 and -5.
(v) Given a = 11, d = -4
First term (a) = 11
Second term (a + d) = 11 + (-4) = 11 – 4 = 7
Third terms (a + 2d) = 11 + 2 (-4) = 11 – 8 = 3
Fourth terms (a + 3d) = 11 + 3 (-4) = 11 – 12 = -1
Hence, first four terms of A.P. are 11, 7, 3 and -1.
First term (a) = 4
Second term (a + d) = 4 + (-3) = 1
Third term (a + 2d) = 4 + 2 (-3) = 4 – 6 = -2
Fourth term (a + 3d) = 4 + 3(-3) = 4 – 9 = -5
Hence, four terms of A.P are 4, 1, -2 and -5.
(v) Given a = 11, d = -4
First term (a) = 11
Second term (a + d) = 11 + (-4) = 11 – 4 = 7
Third terms (a + 2d) = 11 + 2 (-4) = 11 – 8 = 3
Fourth terms (a + 3d) = 11 + 3 (-4) = 11 – 12 = -1
Hence, first four terms of A.P. are 11, 7, 3 and -1.
(vi) Given a = -1.25, d = -0.25
First term (a) = -1.25
Second (a + d) = -1.25 + (-0.25)
= -1.25 – 0.25 = -1.50
Third term (a + 2d)
= -1.25 + 2 (-0.25)
= -1.25 – 0.50 = – 1.75
Fourth term (a + 3d) = -1.25 + 3(-0.25)
= -1.25 – 0.75 = – 2.00
Hence first four terms of A.P. are -1.25, -1.50, -1.75 and -2.00.
First term (a) = -1.25
Second (a + d) = -1.25 + (-0.25)
= -1.25 – 0.25 = -1.50
Third term (a + 2d)
= -1.25 + 2 (-0.25)
= -1.25 – 0.50 = – 1.75
Fourth term (a + 3d) = -1.25 + 3(-0.25)
= -1.25 – 0.75 = – 2.00
Hence first four terms of A.P. are -1.25, -1.50, -1.75 and -2.00.
(vii) Given a = 20, d = 
First Term (a) = 20

First Term (a) = 20

Question 3.
Test A.P for given series of numbers. For an A.P., find its common difference and next four terms also.
(i) 2, , 3,
, 3,  ……
……
(ii)
(iii) a, a2, a3, a4, ……
(iv) √3, √6, √9, √12, ……
(v) √2, √8, √18, √32, …..
(vi) a, 2a, 3a, 4a
(vii) 0.2, 0.22, 0.222 ……
(viii) 3, 3 + √2, 3 + 2√2 , 3 + 3√2, ….
Solution :
(i) Given series 2, , 3,
, 3, 
Here a1 = 2, a2 = , a3 = 3, a4 =
, a3 = 3, a4 = 
Difference between two consecutive terms (d) :


∵ Difference between two consecutive is same, d =
∴ Given series is A.P.
Next four terms are

Hence d = and next four terms of series are 4,
and next four terms of series are 4,  , 5 and
, 5 and 
Test A.P for given series of numbers. For an A.P., find its common difference and next four terms also.
(i) 2,
(ii)
(iii) a, a2, a3, a4, ……
(iv) √3, √6, √9, √12, ……
(v) √2, √8, √18, √32, …..
(vi) a, 2a, 3a, 4a
(vii) 0.2, 0.22, 0.222 ……
(viii) 3, 3 + √2, 3 + 2√2 , 3 + 3√2, ….
Solution :
(i) Given series 2,
Here a1 = 2, a2 =
Difference between two consecutive terms (d) :

∵ Difference between two consecutive is same, d =
∴ Given series is A.P.
Next four terms are

Hence d =
(ii) Given series 
Here a1 =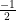 , a2 =
, a2 = 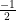 , a3 =
, a3 = 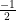 , a4 =
, a4 = 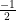
Difference between two consecutive terms (d) :

∵ Difference between two consecutive terms is same, common difference = 0
Thus, given series is a A.P.
Fifth term a5 = Fourth term a4 + Common difference d
= – + 0 = –
+ 0 = –
Sixth term a6 = Fifth term a5 + Common differece d
= – + 0 = –
+ 0 = – 
Seventh term a7 = sixth term a6 + common difference d
= – + 0 = –
+ 0 = –
Eight term a8 = Seventh term a7 + Common difference d
Hence common difference d = 0 and next four terms are – , –
, – , –
, – and –
and –
Here a1 =
Difference between two consecutive terms (d) :

∵ Difference between two consecutive terms is same, common difference = 0
Thus, given series is a A.P.
Fifth term a5 = Fourth term a4 + Common difference d
= –
Sixth term a6 = Fifth term a5 + Common differece d
= –
Seventh term a7 = sixth term a6 + common difference d
= –
Eight term a8 = Seventh term a7 + Common difference d
Hence common difference d = 0 and next four terms are –
(iii) Given series a, a2, a3, a4, …
Here a1 = a, a2 = a2, a3 = a3, a4 = a4
Difference between two consecutive terms d :
a2 – a1 = a2 – a = a(a – 1)
a3 – a2 = a3 – a2 = a2(a – 1)
∵ Difference is not same
i.e., a2 – a1 ≠ a3 – a2
Hence, given series is not an A.P.
Here a1 = a, a2 = a2, a3 = a3, a4 = a4
Difference between two consecutive terms d :
a2 – a1 = a2 – a = a(a – 1)
a3 – a2 = a3 – a2 = a2(a – 1)
∵ Difference is not same
i.e., a2 – a1 ≠ a3 – a2
Hence, given series is not an A.P.
(iv) Given series √3, √6, √9, √12, ……
a1 = √3, a2 = √6, a3 = √9, a4 = √12
Difference between two consecutive terms d :
a2 – a1 = √6 – √3 = √3(√2 – 1) = 0.717
a3 – a2 = √9 – √6 = √3(√3 – √2) = 0.530
∵ Difference is not same
i.e., a2 – a1 ≠ a3 – a2
Thus, Given senes is not A.P
a1 = √3, a2 = √6, a3 = √9, a4 = √12
Difference between two consecutive terms d :
a2 – a1 = √6 – √3 = √3(√2 – 1) = 0.717
a3 – a2 = √9 – √6 = √3(√3 – √2) = 0.530
∵ Difference is not same
i.e., a2 – a1 ≠ a3 – a2
Thus, Given senes is not A.P
(v) Given series is √2, √8, √18, √32, …..
Here a1 = √2, a2 √8,, a3 = √18, a4 = √32
Difference between two consecutive terms d :

∵ Difference is same
Common difference d = √2 and given series is an A.P.
Then 5th term a5 = a4 + d

6th term a6 = a5 + d

7th term a7 = a6 + d

8th term a8 = a7 + d

Hence, common difference d = √2 and next four terms of series are √50, √72, √98 and √128
Here a1 = √2, a2 √8,, a3 = √18, a4 = √32
Difference between two consecutive terms d :

∵ Difference is same
Common difference d = √2 and given series is an A.P.
Then 5th term a5 = a4 + d

6th term a6 = a5 + d

7th term a7 = a6 + d

8th term a8 = a7 + d

Hence, common difference d = √2 and next four terms of series are √50, √72, √98 and √128
(vi) Given series is a, 2a, 3a, 4a,…
Here a1 = a, a2 = 2a, a3 = 3a, a4 = 4a
Difference between two consecutive terms (d) :
a2 – a1 = 2a – a = a
a3 – a2 = 3a – 2a = a
a4 – a3 = 4a – 3a = a
∵ Common difference is same
Thus, common difference d = a and given series is an A.P.
Then 5th term a5 = a4 + d
= 4a + a = 5a
6th term a6 = a5 + d
= 5a + a = 6a
7th term a7 = a6 + d
= 6a + a = 7a
8th term a8 = a7 + d
= 7a + a = 8a
Hence, common difference d = a and next four terms arc 5a, 6a, 7a and 8a.
Here a1 = a, a2 = 2a, a3 = 3a, a4 = 4a
Difference between two consecutive terms (d) :
a2 – a1 = 2a – a = a
a3 – a2 = 3a – 2a = a
a4 – a3 = 4a – 3a = a
∵ Common difference is same
Thus, common difference d = a and given series is an A.P.
Then 5th term a5 = a4 + d
= 4a + a = 5a
6th term a6 = a5 + d
= 5a + a = 6a
7th term a7 = a6 + d
= 6a + a = 7a
8th term a8 = a7 + d
= 7a + a = 8a
Hence, common difference d = a and next four terms arc 5a, 6a, 7a and 8a.
(vii) Given series is
0.2, 0.22, 0.222. 0.2222, …
Hear a1 = 0.2, a2 = 0.22, a3 = 0.222, a4 = 0.2222.
Difference of two consecutive terms (d) :
a2 – a1 = 0.22 – 0.2 = 0.02
a3 – a2 = 0.222 – 0.22 = 0.002
a4 – a3 = 0.2222 – 0.222 = 0.0002
Difference is not same
i.e., a2 – a1 ≠ a3 – a2 ≠ a4 – a3
Hence given series ¡s not AP.
0.2, 0.22, 0.222. 0.2222, …
Hear a1 = 0.2, a2 = 0.22, a3 = 0.222, a4 = 0.2222.
Difference of two consecutive terms (d) :
a2 – a1 = 0.22 – 0.2 = 0.02
a3 – a2 = 0.222 – 0.22 = 0.002
a4 – a3 = 0.2222 – 0.222 = 0.0002
Difference is not same
i.e., a2 – a1 ≠ a3 – a2 ≠ a4 – a3
Hence given series ¡s not AP.
(viii) Given series is 3, 3+√2, 3+2√2, 3+3√2, …….
ie., a1 = 3, a2 = 3+√2, a3 = 3+√2, a4 = 3+√2
Difference between two consecutive terms (d) :

∵ Difference is same.
∴ Common difference d = √2, and given series is an A.P.
Then, fifth term a5 = a4 + d
= 3 + 3√2 + √2
= 3 + √2(3 + 1) = 3 + 4√2
Then, sixth term a6 = a5 + d
= 3 + 4√2 + √2
= 3 + √2(4 + 1) = 3 + 5√2
Then, seventh term a7 = a6 + d
= 3 + 5√2 + √2
= 3 + √2(5 + 1) = 3 + 6√2
Then, Eighth term a8 = a7 + d
= 3 + 6√2 + √2
= 3 + √2(6 + 1) = 3 + 7√2
Hence, common difference d = √2 and next four terms of series are 3 + 4√2, 3 + 5√2, 3 + 6√2 and 3 + 7√2.
ie., a1 = 3, a2 = 3+√2, a3 = 3+√2, a4 = 3+√2
Difference between two consecutive terms (d) :

∵ Difference is same.
∴ Common difference d = √2, and given series is an A.P.
Then, fifth term a5 = a4 + d
= 3 + 3√2 + √2
= 3 + √2(3 + 1) = 3 + 4√2
Then, sixth term a6 = a5 + d
= 3 + 4√2 + √2
= 3 + √2(4 + 1) = 3 + 5√2
Then, seventh term a7 = a6 + d
= 3 + 5√2 + √2
= 3 + √2(5 + 1) = 3 + 6√2
Then, Eighth term a8 = a7 + d
= 3 + 6√2 + √2
= 3 + √2(6 + 1) = 3 + 7√2
Hence, common difference d = √2 and next four terms of series are 3 + 4√2, 3 + 5√2, 3 + 6√2 and 3 + 7√2.
Hope that the Solutions provided here for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Ex 5.1 will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression Ex 5.1 solution drop a comment below and like and share the post.
Thank you.







1 Comments
This notes are very useful
ReplyDelete